A brain lesion diagnosis after a traumatic event like a car accident or a fall changes everything. Suddenly, your medical journey is tied to complex legal questions. The most critical one? How long can you live with a brain lesion? The answer isn’t just about your future health—it’s the foundation of your personal injury claim. Your prognosis directly impacts the compensation you can receive for long-term medical care, lost income, and your quality of life. This article breaks down the medical factors that shape your outlook, empowering you to protect both your health and your rights.
Key Takeaways
- Focus on the specifics of your diagnosis, not just the term “brain lesion”: Your prognosis is shaped by factors like the lesion’s type, grade, and location, along with your personal health—not by statistics alone.
- Proactive treatment is your most powerful tool: Acting on early warning signs and starting treatment promptly gives you access to more effective options, like surgery and radiation, which can directly improve your long-term outcome.
- Build a comprehensive support system: Navigating a diagnosis is easier with support, which includes connecting with patient advocacy groups, clarifying your medical decision-making rights, and seeking legal counsel if your lesion was caused by an injury.
What Does a Brain Lesion Diagnosis Mean?
Hearing the term “brain lesion” can be unsettling, but it’s important to understand what it actually means. Simply put, brain lesions are areas of brain tissue that show signs of injury or damage. As the Cleveland Clinic explains, they are abnormalities that doctors can often “see” on medical imaging scans like an MRI or CT scan. Think of it as a broad, general term that doctors use before they have a more specific diagnosis. It’s not a final answer, but rather the first clue in a medical investigation.
A lesion can be anything from a scar left by an old injury to a tumor or an area affected by a stroke. The discovery of a lesion is the starting point for more investigation. Your medical team will work to figure out exactly what the lesion is, what caused it, and what it means for your health. This process can feel overwhelming, but getting clear answers is essential. If your lesion was caused by a traumatic event, such as a car accident or a fall, understanding your diagnosis is also the first step in exploring your legal options. The path forward depends entirely on the lesion’s specific type, size, and location, which is why the next steps in your medical journey are so critical for both your health and any potential personal injury claim.
Benign vs. Malignant: What’s the Difference?
Once a lesion is identified, one of the first questions your doctor will try to answer is whether it is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). This distinction is crucial because it heavily influences your prognosis and treatment plan. Benign lesions don’t contain cancer cells and typically grow more slowly. According to the Moffitt Cancer Center, benign lesions “generally have a good prognosis, with many people living for many years.” However, even a benign lesion can cause serious problems if it presses on sensitive parts of the brain. Malignant lesions, on the other hand, are cancerous and can be more aggressive. They may grow quickly and spread to other areas of the brain, making them more difficult to treat.
Brain Lesion vs. Concussion: What’s the Difference?
It’s easy to confuse these two terms, but the distinction is important for your medical care and any potential legal claim. Think of a brain lesion as a physical, structural injury to the brain tissue that a doctor can actually see on an imaging scan like an MRI or CT. These are identifiable abnormalities, which could be a bruise on the brain (a contusion) or a scar from a previous injury. A concussion, on the other hand, is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that affects how your brain functions. It happens when a blow to the head causes the brain to jolt, leading to symptoms like headaches, confusion, and dizziness. While a severe impact can certainly cause both a concussion and a lesion, a concussion itself doesn’t always leave visible damage on a scan, making it a functional injury rather than a structural one.
What Are the Common Types and Causes?
Brain lesions can happen for a wide variety of reasons. Sometimes they are the result of a traumatic injury, like a blow to the head from an accident. In other cases, they stem from underlying medical conditions. The list of potential causes is long and includes everything from infections and strokes to immune system disorders like multiple sclerosis and diseases that worsen with age, such as Alzheimer’s. The type and cause of the lesion are just one part of the puzzle. Its location is also incredibly important. For example, the Moffitt Cancer Center notes that “lesions in certain areas of the brain, such as the brainstem, can be more serious and have a lower survival rate” because the brainstem controls vital functions like breathing and your heartbeat. Identifying the cause is key to determining the right course of action, whether that involves medical treatment or seeking justice for an injury caused by someone else’s negligence.
Abscesses
An abscess is a pocket of infection that contains pus and swollen tissue. While they are rare, they can be quite dangerous. According to WebMD, these lesions are often the result of an infection that spreads from a nearby area, like your sinuses or ears. They can also develop after a head injury or surgery, which is an important connection to understand if your lesion appeared after an accident. Because they are caused by bacteria, treatment typically involves antibiotics and sometimes a procedure to drain the abscess. Identifying the source of the infection is a key step in preventing it from happening again and ensuring a full recovery.
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Arteriovenous malformations, or AVMs, are unusual tangles of blood vessels that typically form before birth. The blood vessels in an AVM are weak and can be prone to leaking blood into the brain. They can also disrupt normal blood flow, preventing brain tissue from getting the oxygen it needs. For many people, an AVM goes unnoticed for years, and sometimes the first sign that something is wrong is a seizure. Because they are congenital, they aren’t caused by an injury, but a traumatic event could potentially cause a fragile AVM to rupture, leading to a serious medical emergency.
Cerebral Infarction (Stroke)
A cerebral infarction is the medical term for a stroke, which is one of the most common causes of brain lesions. This happens when brain cells die because they aren’t receiving enough blood. A blockage in an artery, often from a blood clot, is usually the culprit. The resulting damage creates a lesion that is visible on a brain scan. The long-term effects of a stroke depend entirely on which part of the brain was affected and for how long. Quick medical intervention is critical to minimize the damage and improve the chances of a successful recovery from this type of lesion.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic condition where the body’s own immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of the nerves, known as myelin. This damage occurs in the brain and spinal cord, creating lesions that disrupt the communication signals between the brain and the rest of the body. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, from numbness and tingling to problems with balance and coordination. While MS is a lifelong condition, there are many treatments available that can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Beyond a localized abscess, a wide range of other issues can cause inflammation in the brain and lead to lesions. The Mayo Clinic notes that many things can trigger this response, including various infections, problems with the immune system, or even exposure to certain chemicals. Conditions like encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) or meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain) can leave behind damaged tissue. Identifying the underlying cause of the inflammation is the first step toward getting the right treatment, which might include antiviral medications or therapies to calm the immune system.
Genetic Diseases and Structural Issues
Sometimes, brain lesions are linked to genetic conditions or diseases that tend to worsen over time. For example, degenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s can cause changes in the brain that appear as lesions on an MRI. Other inherited conditions can also make someone more susceptible to developing structural abnormalities in their brain. Understanding your family’s medical history can sometimes provide important clues for your doctors as they work to diagnose the cause of your lesion and determine the best path forward for your care.
Medical Treatments
The right treatment for a brain lesion depends entirely on what caused it in the first place. There is no one-size-fits-all approach. For lesions caused by infections, antibiotics or other medications may be all that’s needed. For tumors, whether benign or malignant, treatment might involve a combination of approaches. As WebMD explains, surgery is often an option to remove a lesion, especially if it is accessible and causing significant symptoms. Radiation and chemotherapy are other common treatments, particularly for cancerous lesions. Your medical team will develop a personalized plan based on your specific diagnosis.
Unknown Causes
It can be frustrating to hear, but sometimes doctors can’t pinpoint the exact cause of a brain lesion. After all the tests and scans, the origin may remain a mystery. This is more common than you might think. In these situations, doctors will often recommend a “watch and wait” approach, using regular imaging scans to monitor the lesion for any changes in size or shape. If the lesion remains stable and doesn’t cause any symptoms, no immediate treatment may be necessary. While the uncertainty can be difficult, it’s important to remember that not every lesion requires aggressive intervention.
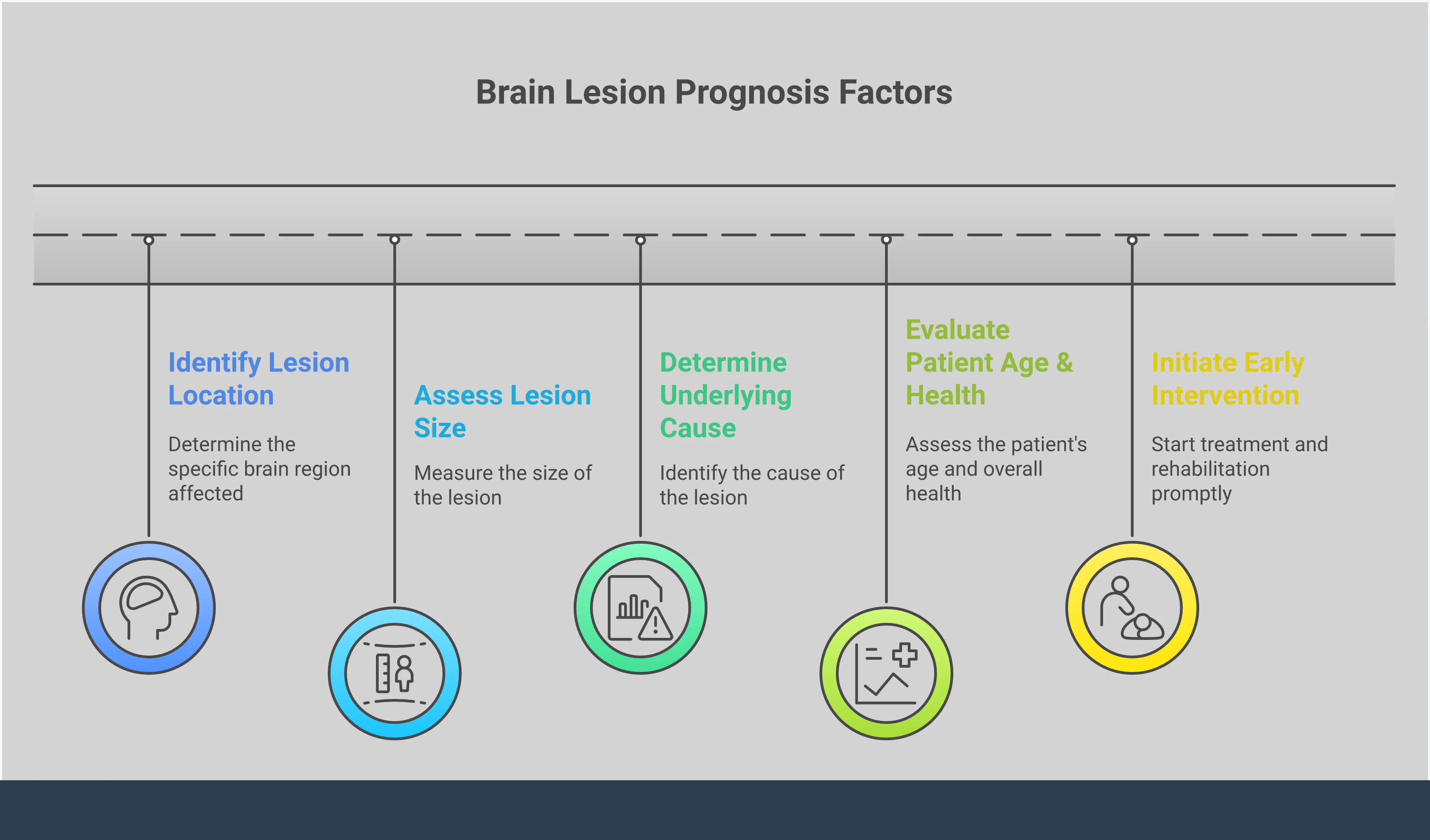
What Affects Your Brain Lesion Prognosis?
When you receive a diagnosis, one of the first questions is often about the future. A prognosis for a brain lesion isn’t a single, definite answer; it’s a forecast based on several interconnected factors. Think of it less as a fixed destination and more as a roadmap with different possible routes. Your medical team will consider the unique characteristics of the lesion, your personal health profile, and the treatments available to give you the most accurate outlook possible. Understanding these elements can help you feel more informed and prepared for the conversations ahead.
Why Lesion Type, Grade, and Location Matter
The nature of the lesion itself is the most significant factor in determining a prognosis. A benign (non-cancerous) lesion generally has a much better outlook than a malignant (cancerous) one. Doctors also “grade” tumors based on how abnormal the cells look and how quickly they are likely to grow. For example, some slow-growing benign tumors have a five-year survival rate of over 90%. In contrast, a high-grade, aggressive tumor like a glioblastoma has a much lower survival rate. The lesion’s location also matters. If it’s in an area that’s difficult to operate on or controls vital functions, treatment can be more complex.
How Your Age and Health Play a Role
Your personal health profile plays a crucial role in your prognosis. Generally, younger individuals tend to have a more favorable outcome. According to Cancer Research UK, people younger than 40 often have a better outlook than older adults. Your overall health is another key piece of the puzzle. If you are in good health without other serious conditions, your body may be stronger and more resilient to handle intensive treatments like surgery or chemotherapy. A strong foundation of health gives you a better chance to recover from treatment and manage side effects, which can positively influence your long-term prognosis.
Why Early Detection Makes a Difference
The timing of your diagnosis can make a huge difference. Finding a brain lesion early is critical because it often means more treatment options are available and the lesion may be smaller and easier to manage. When a lesion is detected before it has grown large or spread, treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy tend to be more effective. This is why it’s so important to see a doctor if you experience persistent or unusual symptoms like severe headaches, seizures, or changes in vision or personality. Acting quickly can significantly improve your chances of a successful outcome and a better long-term prognosis.
Can Your Lifestyle Choices Affect Your Prognosis?
While lifestyle choices alone can’t determine your prognosis, they can certainly support your overall well-being during a challenging time. Being in good physical condition helps your body withstand the rigors of treatment and can aid in recovery. Maintaining a balanced diet, getting gentle exercise as approved by your doctor, and avoiding smoking can contribute to your general health. These habits support your immune system and can improve your energy levels and mental state. Think of it as giving your body the best possible resources to fight. Your overall health is a key component of your brain lesion recovery journey.
Understanding Life Expectancy with a Brain Lesion
Understanding the long-term outlook for a brain lesion can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to remember that life expectancy varies widely. The single most significant factor is the type of lesion you have—whether it’s benign (non-cancerous), malignant (cancerous), or metastatic (cancer that has spread from elsewhere). Each category carries a different prognosis, and knowing which one you’re dealing with is the first step in understanding what lies ahead. While statistics provide a general picture, they don’t define your individual path.
What’s the Outlook for Benign Brain Lesions?
Hearing the word “benign” is often a relief, as it means the lesion is not cancerous. For many people with benign brain tumors, the outlook is quite positive. With proper treatment and consistent monitoring, it’s possible to live a long and full life. For example, for a common type called a benign meningioma, about 80% to 90% of people live for at least 10 years after their diagnosis. While these lesions don’t invade nearby tissue like cancerous ones do, they can still cause serious problems by pressing on parts of the brain. That’s why a clear treatment plan is essential for managing symptoms and ensuring the best possible outcome.
The Prognosis for Malignant Brain Tumors
A malignant, or cancerous, brain tumor presents a more serious challenge, and the prognosis can be much more unpredictable. Survival rates depend heavily on the specific type and grade of the tumor. For glioblastoma, one of the most aggressive types, the average five-year survival rate is around 15%. For other types, like anaplastic astrocytoma, the outlook is slightly better, with a five-year survival rate of over 20%. These numbers can be difficult to process, but they highlight the importance of aggressive treatment and ongoing medical research that continues to improve survival for brain tumours.
What to Expect with Metastatic Brain Lesions
Metastatic brain lesions occur when cancer from another part of the body—like the lungs, breast, or skin—spreads to the brain. Unfortunately, this is a very serious diagnosis, and the prognosis is often poor. Because the cancer is already advanced, treatment focuses more on managing symptoms and improving quality of life rather than a cure. The average survival time for someone with brain metastases is typically between seven and 24 weeks. These survival statistics reflect the advanced stage of the disease, making every moment with loved ones even more precious.
Why Statistics Don’t Tell the Whole Story
It’s crucial to remember that statistics are just averages based on large groups of people—they are not your personal destiny. Your individual prognosis can be very different based on several key factors. The specific type and grade of the tumor, its location in the brain, and whether it can be completely removed with surgery all play a huge role. Your age and overall health are also significant. A younger, healthier person may respond better to treatment than someone who is older or has other medical conditions. Ultimately, your brain tumor survival rate is unique to you, and your medical team can provide the most accurate outlook based on your specific situation.
How Doctors Diagnose Brain Lesions
After an initial scan reveals a brain lesion, your medical team’s next job is to figure out exactly what it is. This diagnostic phase is a methodical process where doctors gather clues to build a complete picture of your health. They use a combination of advanced imaging and other tests to understand the lesion’s characteristics, its cause, and what it means for your future. Getting a precise diagnosis is the most important step, as it dictates your treatment plan and provides the clarity needed to move forward, both medically and, if your injury was caused by an accident, legally.
Diagnostic Imaging and Tests
To get a closer look at a brain lesion, doctors rely on specialized tests that go beyond a standard MRI or CT scan. These tools help them understand the lesion’s behavior at a cellular level, which is key to determining whether it is benign or malignant. This detailed information is essential for creating an effective treatment strategy tailored to your specific situation. Two common tools in this process are PET scans and blood tests, each offering a unique piece of the puzzle.
PET Scans
A brain positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a powerful imaging test that helps doctors see how the cells in your brain are functioning. Before the scan, you’ll receive a small amount of a radioactive substance called a tracer, which travels through your bloodstream to your brain. As the PET scanner rotates around you, it creates a picture showing where your brain cells are using glucose for energy. Malignant tumor cells are highly active and use more glucose than healthy cells, so they show up brighter in the final image. This makes PET scans incredibly useful for helping doctors detect cancer and determine the best course of treatment.
Blood Tests
While a blood test can’t take a picture of a brain lesion, it provides vital information about your overall health and can offer clues about the lesion’s cause. Your doctor may order blood work to check for signs of infection, inflammation, or other underlying conditions that can lead to abnormalities in the brain. For example, certain proteins or antibodies in the blood can point to an autoimmune disorder like multiple sclerosis, which is a common cause of brain lesions. These tests help rule out other potential causes and give your medical team a more complete understanding of your health, ensuring your diagnosis is as accurate as possible.
How Treatment Can Improve Your Prognosis
Receiving a brain lesion diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to remember that your prognosis is not set in stone. Modern medicine offers powerful treatments that can significantly alter the course of your condition and improve your quality of life. The right treatment plan is highly personalized, depending on the lesion’s type, size, and location, as well as your overall health. Your medical team will likely consist of specialists like neurologists, neurosurgeons, and oncologists who work together to map out the best path forward for you.
The primary goals of treatment are to remove or destroy the lesion, relieve symptoms like headaches or seizures, and prevent further growth. The main strategies include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, which are often used in combination to attack the problem from multiple angles. By taking proactive steps and working closely with your doctors, you can directly influence your outcome. Understanding these options is the first step toward taking control of your health journey and fighting for the best possible prognosis.
How Effective Is Surgical Removal?
For many types of brain lesions, especially tumors, surgery is the primary line of defense. The main goal of a surgical procedure is to remove as much of the lesion as possible without harming the surrounding healthy brain tissue. This process, known as resection, can have a massive impact on your prognosis. In cases of benign tumors, complete removal can sometimes be a complete cure. For malignant lesions, removing the bulk of the tumor can immediately relieve pressure on the brain, reduce symptoms, and make subsequent treatments like radiation or chemotherapy much more effective. Your neurosurgeon will use advanced imaging techniques to plan the safest and most thorough approach.
The Role of Radiation and Chemotherapy
When surgery isn’t possible or can’t remove the entire lesion, radiation and chemotherapy become crucial tools. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to precisely target and destroy abnormal cells while minimizing damage to nearby tissue. Chemotherapy involves powerful drugs, taken orally or intravenously, that travel through the bloodstream to kill fast-growing cells throughout the body. Both of these treatments can significantly improve survival rates for patients. They are effective at shrinking tumors that can’t be operated on, eliminating any microscopic cells left behind after surgery, and slowing down the progression of the lesion, giving you more time and a better quality of life.
Why Doctors May Recommend Combined Treatments
Often, the most effective strategy doesn’t rely on a single method but on a combination of treatments. Think of it as a coordinated attack on the lesion. For example, a patient might first have surgery to remove the majority of a tumor. This is often followed by a course of radiation to target any residual cells that were too small or difficult to remove surgically. Chemotherapy might be added to the plan to address any cells that could have spread. This multi-faceted approach ensures that the lesion is being fought on all fronts, which can lead to better long-term outcomes. Your medical team will create a tailored plan that sequences these treatments for maximum impact.
Monitoring and Non-Invasive Options
Aggressive treatments like surgery and radiation aren’t always the immediate first step. In some situations, a more conservative approach is the wisest course of action. This is especially true for lesions that are small, slow-growing, or not causing any disruptive symptoms. Your medical team might decide that the risks of an invasive procedure outweigh the potential benefits, at least for the time being. Instead, they may opt for careful observation or recommend simple, non-invasive measures that give your body the chance to heal on its own. This path prioritizes your quality of life while keeping a close eye on the situation.
The “Wait and See” Approach
Sometimes, the best initial plan is to do nothing at all—at least in terms of active treatment. This is often called the “wait and see” or active surveillance approach. If a lesion isn’t causing problems or growing, your doctor might recommend simply monitoring it with regular checkups and imaging scans. According to WebMD, this strategy allows your medical team to track any changes over time without subjecting you to unnecessary procedures. While it can feel unsettling to know a lesion is there, this careful observation is a proactive and common medical strategy for many slow-growing or stable conditions.
Rest and Recovery for Mild Lesions
For mild lesions, such as those resulting from a concussion after a fall or car accident, the brain often has a remarkable ability to heal itself. In these cases, the primary treatment is simply rest. The Cleveland Clinic explains that giving your brain time to recover, free from physical and mental strain, is essential. This means avoiding strenuous activities and getting plenty of sleep. Following your doctor’s orders for rest is not a passive step; it’s the most important thing you can do to support your body’s natural healing process and prevent further injury.
When Lesions Cannot Be Treated
It’s a difficult reality that some brain lesions cannot be cured. This may be because the lesion is located in a delicate, inoperable part of the brain, is too severe, or is the result of an incurable disease. When a cure isn’t possible, the focus of medical care shifts from eliminating the lesion to managing symptoms and maximizing your quality of life. This approach, often called palliative care, is about providing comfort, relieving pain, and offering emotional and spiritual support. During this time, it becomes incredibly important to have open conversations with your loved ones and ensure your affairs are in order. Addressing legal matters, such as estate planning, can provide peace of mind for both you and your family, allowing you to focus on what truly matters. If you need guidance, exploring your options with a legal professional can clarify the steps needed to protect your wishes and your loved ones. You can learn more about different practice areas that can help you prepare for the future.
Why the Timing of Treatment Matters
When it comes to a brain lesion, time is of the essence. Seeking prompt medical attention and starting treatment as soon as possible after a diagnosis can make a world of difference. Early intervention often means you have more available treatment options, as the lesion may be smaller and less complex to address. The sooner treatment begins, the better the chance of preventing the lesion from growing, spreading, or causing irreversible damage to critical brain functions. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms, don’t wait. Getting a swift and accurate diagnosis is the most important step you can take toward securing a more favorable prognosis and getting the support you need.
Which Symptoms Need Immediate Medical Attention?
When you’re dealing with a potential brain lesion, it’s easy to second-guess what you’re feeling. Is that headache just stress, or is it something more? Knowing which symptoms are red flags can help you act quickly and confidently. Some signs of a brain lesion can develop gradually, while others appear suddenly and demand immediate medical help. Listening to your body and understanding the difference is one of the most important things you can do for your health.
It’s completely normal to feel uncertain or even dismiss minor changes, but your awareness is your strongest tool. The key is to notice what’s new or different for you. A symptom that seems small at first could be part of a larger pattern. By learning to recognize both subtle shifts and urgent signals, you empower yourself to seek the right care at the right time. If you or a loved one experience any of the symptoms below, it’s time to talk to a doctor. Getting a prompt and accurate diagnosis is the first step toward creating an effective treatment plan and protecting your well-being.
What Are the Early Warning Signs?
Early symptoms of a brain lesion can be subtle, but paying attention to persistent changes is key. Think of these as your body’s early warning system. One of the most common signs is a new pattern of headaches that are unusually severe or simply won’t go away. Other early warning signs can include unexplained seizures, gradual shifts in your memory or thinking, and new problems with your vision or balance. You might also notice weakness or numbness in your limbs that you can’t explain. If any of these symptoms stick around and disrupt your daily life, don’t just hope they’ll disappear. Schedule an appointment with your doctor to get them checked out.
How Symptoms Relate to Lesion Location
The brain isn’t one big, uniform organ; it’s a collection of highly specialized areas, each with a specific job. Because of this, the symptoms you experience from a brain lesion are a direct clue to its location. Think of it like a power outage in a city—if the lights go out in one neighborhood, you know the problem is likely with the substation that serves that specific area. Similarly, if you’re having trouble with your vision, doctors will look closely at the part of your brain that processes sight. Understanding this connection can help you make sense of your symptoms and communicate more effectively with your medical team.
Frontal Lobe Lesions
Your frontal lobe is essentially your brain’s command center. It manages your personality, decision-making, and emotional control. When a lesion develops here, often due to head trauma from an accident, the changes can be profound. According to the National Institutes of Health, a frontal lobe syndrome can cause dramatic shifts in personality, making someone who was once calm and considerate suddenly impulsive or irritable. You might also notice difficulty with planning, solving problems, or controlling social behavior. These changes can be incredibly challenging for both the individual and their family, fundamentally altering a person’s identity and relationships.
Parietal Lobe Lesions
The parietal lobe is responsible for processing sensory information and helping you understand the world around you. It integrates signals related to touch, temperature, and pain, and it’s also crucial for spatial awareness. If a lesion forms in this area, you might struggle with coordination and balance. As Physiopedia explains, this can lead to problems with recognizing objects by touch or even being aware of your own body parts. For example, you might have trouble buttoning a shirt or navigating through a familiar room, as your sense of where you are in space becomes distorted.
Occipital Lobe Lesions
Located at the back of the brain, the occipital lobe is the primary center for vision. Any damage here directly impacts your ability to see. Symptoms can range from blurred vision or blind spots to more complex issues like difficulty recognizing faces or colors. In some cases, a person might even experience visual hallucinations. Because this part of the brain is so specialized, lesions in the occipital lobe almost exclusively produce visual symptoms, making it one of the more straightforward areas to diagnose based on the signs you’re experiencing.
Cerebellum Lesions
The cerebellum, situated at the base of the brain, is the master of coordination and balance. It fine-tunes your motor movements, allowing you to walk, run, and perform delicate tasks with precision. When a lesion affects the cerebellum, these abilities can be severely compromised. Common symptoms include tremors, an unsteady and clumsy walk, and a general lack of coordination. You might find it difficult to perform simple actions like writing or picking up a small object. These issues with motor control can be incredibly frustrating and can significantly impact your independence and daily activities.
Brainstem Lesions
The brainstem is the connection between your brain and your spinal cord, and it controls the most essential functions for survival—breathing, heart rate, and consciousness. Because of its critical role, a lesion in the brainstem is extremely serious. Symptoms can appear suddenly and may include severe dizziness or vertigo, difficulty swallowing, double vision, and slurred speech. Any injury or lesion in this area requires immediate medical attention, as it can quickly become life-threatening. The severity of these symptoms underscores the devastating impact a traumatic injury can have on the brain’s most vital structures.
How to Spot Symptoms That Are Getting Worse
Not all brain lesions cause immediate problems. Some, especially those that are slow-growing, can exist for months or even years without you knowing. Symptoms often start only when the lesion becomes large enough to press on or interfere with surrounding brain tissue. You might notice a mild symptom, like occasional dizziness, that slowly becomes more frequent or intense over weeks or months. Keeping a simple log of your symptoms—what they are, when they happen, and how they change—can be incredibly helpful for your doctor. This information provides a clearer picture of what’s happening and can help guide the diagnostic process more efficiently.
When Should You Go to the ER?
Some symptoms are not just warnings; they are emergencies. If you notice any of the following signs in yourself or someone else, you need to seek medical care right away. Call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room for a sudden, severe headache that feels like the worst you’ve ever had, or any new and unexplained changes to your vision. Other critical symptoms that require immediate attention include seizures that last longer than five minutes, losing consciousness after a head injury, or sudden, drastic changes in behavior or awareness. If these symptoms appear after an automobile accident or other personal injury, getting immediate medical care is the top priority.
Can You Prevent Brain Lesions?
While you can’t control every factor that might lead to a brain lesion, like genetics, you have more power than you might think. Many causes are tied to lifestyle choices, underlying health issues, and traumatic injuries. Focusing on what you can influence is an empowering way to protect your long-term health. By taking proactive steps to safeguard your brain and manage your overall well-being, you can significantly reduce your risk for certain types of lesions.
Protective Measures and Healthy Habits
Some of the most effective ways to prevent brain lesions are also the most straightforward. Protecting your head from injury is paramount. This means always wearing a helmet during activities with a risk of head trauma, like riding a bike or playing contact sports, and taking precautions to prevent falls at home. Beyond physical safety, general wellness plays a huge role. Staying active, eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and keeping your mind engaged all contribute to a healthier brain. These healthy habits support good circulation and reduce inflammation, creating an environment where your brain can thrive and better defend against potential damage.
Managing Existing Health Conditions
Many brain lesions, particularly those caused by strokes or inflammation, are linked to other health problems. This is why actively managing any existing medical conditions is a critical form of prevention. Working closely with your doctor to control issues like high blood pressure, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders can dramatically lower your risk. It’s essential to follow your prescribed treatment plan, attend regular check-ups, and communicate any new or worsening symptoms to your healthcare provider. By being proactive about your health, you can address potential problems before they escalate, giving you the best chance to avoid complications that could affect your brain.
Finding Support for You and Your Family
A brain lesion diagnosis is a life-altering event that extends beyond the individual to affect the entire family. Facing this journey can feel isolating, but you don’t have to do it alone. A wide range of support services and programs are available to help you and your loved ones manage the physical, emotional, and financial challenges that come with treatment and recovery. Finding the right support can make a significant difference in your quality of life and overall well-being.
Facing Common Hurdles in Treatment and Recovery
The path through treatment and recovery is often filled with practical challenges. You might be dealing with complex medical information, insurance paperwork, and unexpected costs. Fortunately, many organizations offer resources to help. You can find programs that provide financial assistance for treatment-related expenses, transportation to appointments, and lodging for family members. Educational materials and workshops can also help you better understand the diagnosis and treatment options, empowering you to make informed decisions alongside your medical team. These patient resources are designed to ease the burden so you can focus on healing.
Coping with the Cognitive and Emotional Impact
A brain lesion diagnosis carries a heavy emotional weight for both patients and caregivers. It’s completely normal to feel a mix of fear, anxiety, and uncertainty. Connecting with others who have walked a similar path can be incredibly comforting. The American Brain Tumor Association offers mentor programs that pair you with someone who understands what you’re going through. Professional counseling, support groups, and therapy are also vital resources for processing emotions and developing coping strategies. Taking care of your mental and emotional health is a critical part of the overall treatment plan.
How to Build Your Support System
Caregivers are the unsung heroes in any health crisis, but their own well-being can often be overlooked. The stress of managing appointments, providing care, and offering emotional support can be exhausting. It’s essential for family members and care partners to find their own support systems. Many hospitals and non-profits offer dedicated caregiver support groups, both in-person and online, where you can share experiences and advice. Family counseling can also provide a safe space for everyone to communicate their fears and needs, strengthening your ability to face challenges together as a team.
What to Expect from Rehab and Long-Term Care
Recovery doesn’t end when active treatment does. Rehabilitation is often a key step in regaining skills and improving your quality of life. Depending on your needs, this may include physical therapy to rebuild strength, occupational therapy to adapt daily activities, and speech therapy to address communication challenges. Non-profit patient advocacy organizations are excellent sources of information for finding qualified therapists and understanding long-term care options. These groups can help you plan for the future and connect you with the ongoing support needed to live as fully as possible.
Understanding Your Rights After a Diagnosis
Receiving a brain lesion diagnosis is a life-altering event that immediately shifts your focus to your health, treatment options, and recovery. It’s a time filled with uncertainty and a whirlwind of appointments and information. While your medical journey is the absolute priority, understanding your legal rights during this period can provide a crucial sense of stability and control. Knowing where you stand legally isn’t about adding more stress; it’s about empowering yourself and your family to make clear, informed decisions when it matters most. It ensures you can access the best possible care, that your personal wishes for that care are respected, and that your family’s financial future is protected, especially if your lesion was caused by someone else’s negligence.
Navigating the healthcare system can be overwhelming, but you have fundamental rights as a patient. Similarly, planning for the future through legal documents like advance directives can lift a heavy burden from your loved ones. And if your diagnosis is linked to a traumatic event like a car accident or a slip and fall, you have the right to seek justice and compensation. Exploring these legal avenues provides the resources you need to focus on what’s truly important: your health and well-being. Taking proactive steps to understand your rights can make a significant difference in your journey, offering peace of mind and a solid foundation for the road ahead. You can learn more about the different legal services that can support you during this time.
Do You Have a Right to Specialized Care?
After a diagnosis, you have the right to receive specialized medical care tailored to your specific condition. This includes access to neurologists, surgeons, and oncologists, as well as the right to seek a second opinion to ensure you’re comfortable with your treatment plan. Comprehensive care, however, extends beyond the operating room or chemotherapy suite. It’s important to remember that a wide range of support services are available to help you and your family manage the physical, emotional, and financial challenges that come with a serious diagnosis. Don’t hesitate to ask your medical team for referrals to patient advocates, mental health counselors, support groups, and financial advisors. These resources are designed to provide a holistic support system, helping you feel less alone and more equipped to handle every aspect of your treatment and recovery.
Who Makes Medical Decisions for You?
Thinking about who will make medical decisions for you if you become unable to is a difficult but essential conversation to have. If your condition impacts your ability to communicate your wishes, having legal documents in place ensures your voice is still heard. A healthcare power of attorney is a document that lets you designate a trusted person to make these decisions on your behalf. This is a challenging experience, and fortunately, there are resources available to help you and your family prepare for these conversations. Formalizing your preferences through advance directives not only gives you control over your care but also provides invaluable clarity and guidance for your family, relieving them of the burden of guessing what you would have wanted during an already stressful time.
Can You Get Compensation for an Injury-Caused Lesion?
If your brain lesion was caused by a traumatic injury—such as from a car crash, a workplace accident, or a fall on someone else’s property—you may be entitled to financial compensation. This compensation is meant to cover not just your immediate medical bills but also future care, lost wages from being unable to work, and the significant pain and suffering you’ve endured. Filing a brain injury claim requires several critical steps to secure the full amount you deserve. Because these cases are complex and insurance companies often try to minimize payouts, working with a personal injury lawyer is essential. An experienced attorney will protect your rights, gather the necessary evidence, and fight for a fair settlement, allowing you to focus completely on your recovery. If you believe your injury was caused by another’s negligence, it’s important to seek legal advice promptly.
Related Articles
- How to Find the Best Premises Liability Attorney Near Me
- Do You Need a Premises Liability Lawyer? A Practical Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the first thing I should do if I’m worried about my symptoms? The most important step is to see a doctor right away. Don’t dismiss persistent or unusual symptoms like severe headaches, seizures, or sudden changes in your vision or balance. Getting a prompt medical evaluation is critical because early detection can significantly improve your outcome by opening up more treatment options. Your health is the top priority, and a clear diagnosis is the first step toward getting the care you need.
Does a brain lesion diagnosis automatically mean the worst? Not at all. The term “brain lesion” is a very general starting point, not a final verdict. Your long-term outlook depends entirely on specific factors like the lesion’s type (benign or malignant), its size, and its location in the brain. Many benign lesions can be managed effectively, allowing people to live long, full lives. Your medical team will give you a personalized prognosis based on your unique situation.
How do doctors figure out what type of brain lesion I have? The process usually starts with medical imaging, like an MRI or CT scan, which gives doctors a detailed picture of your brain. These scans reveal the lesion’s location and size. To determine the exact type of cells involved, your doctor might recommend a biopsy, where a small tissue sample is removed and examined. This detailed information is essential for creating the most effective treatment plan for you.
What should I do if my brain lesion was caused by an accident? Your first priority is always to follow your medical team’s treatment plan. Once your immediate health is stable, it’s wise to understand your legal options. If your injury was the result of someone else’s negligence, like in a car crash or a fall, you may be entitled to compensation. This can cover medical bills, lost wages, and future care. Speaking with a personal injury attorney can help you protect your rights and ensure you have the financial resources needed for your recovery.
This is so overwhelming for my family. How can we cope? It’s completely normal for a diagnosis like this to affect the entire family. Open communication is key. It’s also important to remember that you don’t have to go through this alone. Lean on support systems like hospital social workers, patient advocacy groups, and professional counselors. These resources can provide emotional support for everyone, help with practical challenges, and connect you with others who understand what you’re experiencing. Facing this as a team makes the journey more manageable.